Virtually every visitor to historic Lexington will start at the Battle Green, the site of the first fight and the ‘Shot Heard ‘Round the World” on the British’ fateful march to capture Colonial military supplies stored in Concord. This short video provides useful context, military dispositions, and pictures of the attractions on and surrounding Lexington Battle Green.
Enjoy.
[embedplusvideo height=”300″ width=”450″ editlink=”http://bit.ly/1eWpJmb” standard=”http://www.youtube.com/v/TMrDDcpeG_4?fs=1&hd=1″ vars=”ytid=TMrDDcpeG_4&width=450&height=300&start=&stop=&rs=w&hd=1&autoplay=0&react=1&chapters=¬es=” id=”ep7250″ /]
Introduction to Lexington Battle Green
Musket Firing Demo at Minuteman National Historical Park
Attended a wonderful 3.5 hour walk, led by Ranger David Hannigan, of the Battle Road between Concord and Lexington. When passing by the Hartwell Tavern, we had the opportunity to view this Musket Firing Demo by Ranger Charlie Webster. It was done according to the standard British 1764 Manual of Arms, which was used by both British and Colonial forces.
[embedplusvideo height=”281″ width=”450″ editlink=”http://bit.ly/16CebLT” standard=”http://www.youtube.com/v/1ZzBaBad75Q?fs=1&hd=1″ vars=”ytid=1ZzBaBad75Q&width=450&height=281&start=&stop=&rs=w&hd=1&autoplay=0&react=1&chapters=¬es=” id=”ep8490″ /]
Click for the Minuteman National Historical Park schedule of events. The 3.5 hour Battle Road Walk, wonderful for those interested in detailed Battle information, is given monthly, June through October.
Prospect Hill – Key Fortress in the Patriot Lines
Select your language to auto-translate:
When on the night of April 18th the British left Boston on their fateful expedition to capture Patriot munitions in Concord and the “shot heard round the world,” they marched by a hill just outside of Union Square, in what today is the city of Somerville. In 1775, Somerville was part of Charlestown and was located “just beyond the neck” that separated the Charlestown peninsula from the mainland. The hill is called Prospect Hill, and it was to play a key role in America’s fight for freedom from Great Britain.
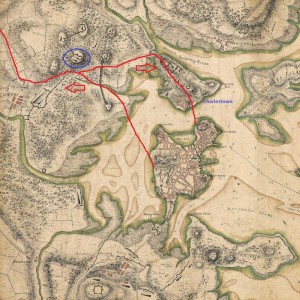 In the British retreat back to Boston on April 19th, they diverted to go via Charlestown and they again passed by Prospect Hill, but this time in hurried flight and under constant fire from American militia that had gathered from over 30 miles away. (Prospect Hill was one of the last landmarks to pass before the British could reach sanctuary in Charlestown.) There was a major skirmish at the foot of the hill, leading to death on both sides. At the end of the day, American troops were posted on the hill to observe the British as they ferried troops across the harbor between Charlestown and Boston.
In the British retreat back to Boston on April 19th, they diverted to go via Charlestown and they again passed by Prospect Hill, but this time in hurried flight and under constant fire from American militia that had gathered from over 30 miles away. (Prospect Hill was one of the last landmarks to pass before the British could reach sanctuary in Charlestown.) There was a major skirmish at the foot of the hill, leading to death on both sides. At the end of the day, American troops were posted on the hill to observe the British as they ferried troops across the harbor between Charlestown and Boston.
Two months later, immediately after the Battle of Bunker Hill, Prospect Hill was the sight of major American fortification and became the central position of the Continental Army’s chain of emplacements north of Boston. Its height and commanding view of Boston and the harbor had tremendous strategic value and the fortress became known as the “Citadel”.
On July 1st, 1776, George Washington had the new “Grand Union Flag,” the first official flag that represented the united colonies, raised at the top of the Hill. It combined the familiar British Union Flag with 13 red and white stripes. (It was not until 1777 that the more familiar flag with stripes and thirteen stars was adopted.) During the winter of 1777-8, after his defeat at Saratoga, General Burgoyne and 2,300 of his troops were housed as prisoners of war in barracks on the hill. In 1903, a castle shaped monument was erected at the sight of the primary American fortifications. Today, the view of Boston and the surrounding towns is still impressive.
In 1903, a castle shaped monument was erected at the sight of the primary American fortifications. Today, the view of Boston and the surrounding towns is still impressive.
View Prospect Hill – Site of Fighting and Patriot Fortifications in a larger map
Jason Russell House – Site of the Bloodiest Fighting in the Battles of Lexington & Concord
Select your language to auto-translate:
Arlington, then known by the Native American name of Menotomy, was the sight of the most intense fighting during the British retreat after the Battles of Lexington and Concord. About half of those who lost their lives, about 25 of the Americans and 40 of the British, died in Arlington. Of the American causalities, about half of the deaths took at the Jason Russell House.
The house was built by Jason Russell between 1740 and 1745, but had been doubled in size by the time of the 1775 battle. As it is located on Concord Road (now Massachusetts Avenue), the main street connecting Cambridge and Concord, it was strategic and was gathering site for Minute Men, as well as Jason and some of his neighbors, who wished to contest the British retreat. At the time the British were passing, about two dozen men had gathered around the Russell house and created a mini-fortress.
Although the group had effectively fortified themselves to be able to take pot shots at the main British column marching down Concord Road, they left themselves open to the flankers, who caught them by surprise. Trying to reach sanctuary in his house, Russell was shot down and died on his doorstep. Eight Patriots were cornered and bayoneted. About eight other Patriots effectively barricaded themselves in the basement. Although there were multiple British casualties, a total of twelve Patriots died in and around the Russell house – making this the bloodiest spot in a bloody day.
Bullet holes can still be seen in several parts of the house, which is open for visitors and part of the Arlington Historical Society. There is a wonderful and detailed write-up of the house and its history as part of the Historic New England’s Old-Time New England Articles section, available here.
View Jason Russell House – Site of the Bloodiest Fighting in the Battles of Lexington & Concord in a larger map
Cambridge, Lexington & Concord: Freedom Trail Day Trips
Select your language to auto-translate:
Cambridge
Cambridge, capitalized as “Newe Town” in 1632, is about five miles up the Charles River from Boston. It was established soon after Boston’s Puritan settlers arrived to provide a safe haven in event of an attack on the coastal Boston. The original village was located at the first convenient river crossing west of Boston, at what is now Harvard Square. Harvard College was founded here in 1636. The town served as the headquarters for the Patriot troops during the Siege of Boston.
Most tourists will want to visit Harvard University and take in the Revolutionary sites around Harvard Square. The best way to visit the area in a few hours is via a walking tour, which is offered by several companies.
I can recommend those from Cambridge Historical Tours, phone 617.520.4030, website here. The basic 90 minute walk covers the University and general Cambridge history; $12 for adults, $7 for children. For those interested in the Revolutionary-era, add the Tory Row option which extends the walk by ½ hour and costs an additional $3.
There are Free Student-Led & Self-Guided Walking Tours of Harvard Yard available directly from Harvard. For the self-guided tours, click here (includes a PDF map and audio files). For mobile phone versions of the self-guided tour, click here. For information about the free student-led tours, click here.
The Longfellow House, run by the National Park Service, is on Tory Row and is only a short walk from Harvard Square. In addition to being the home of poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, it was George Washington’s headquarters during the Siege of Boston. The NPS offers seasonal ranger-led tours, talks, and neighborhood walks. For hours and tour times, access the website here or call 617-876-4491. Admission is free.
Public transportation from Boston is easy and quick via the MBTA Red line to the Harvard Square station.
Lexington & Concord
The nearby colonial towns of Lexington and Concord were the sites of the first significant battle of the American Revolution. A visit is highly worthwhile and an easy 1/2 to full day trip from Boston. Each year Massachusetts celebrates Patriots Day, around the April 19th anniversary of the battle, with reenactments and parades at many stops along the battle’s route. For more on the Battles of Lexington and Concord, click here. For a YouTube video intro to Lexington Battle Green, click here.
Most of the Lexington sites center on the Lexington Battle Green, at the site of the first skirmish. For maps and information, start at the Visitor Center, located next to the Battle Green. For Lexington information, click here or call 781-862-1450. There is a downloadable self-guided walking tour of the Battle Green area along with other information from the Lexington Historical Society, to download click here. Call 781-862-1703 to reach the Historical Society directly, website here. The Historical Society runs the Hancock-Clark House, Buckman Tavern, and Munroe Tavern. All offer tours by excellent docents and each offers a unique perspective. The Tourism Committee also runs free tours given by costumed guides, spring through fall . The narrated hop-on/off Liberty Ride, which runs to all the major sites from Lexington to Concord, is a fun way to travel and learn history at the same time.
Important visitor sites close to the Battle Green include the Minuteman Statue (paradoxically, Lexington never had minutemen, only militia), the Buckman Tavern (where the Minutemen gathered just prior to the battle), the Hancock-Clarke House (where Samuel Adams and John Hancock stayed the night before the battle), and the Old Belfry. The Historical Society runs the Hancock-Clark House, Buckman Tavern, and Munroe Tavern. All offer tours by excellent docents and each offers a unique perspective.
Just east of Lexington town center is the Munroe Tavern. The Munroe Tavern was the site of the British headquarters and field hospital during their retreat back to Boston. A packaged ticket for admission to the Munroe Tavern, the Hancock-Clarke House and the Buckman Tavern is available at any of the three houses: $12 for adults and $8 for children 6-16. Individual house admissions are $7 and $5 respectively. Contact the Lexington Historical Society to confirm the operating hours, which vary by season.
Concord was the site of the battle at North Bridge, but if you have time, it has a lot more to offer. For visitor information in the town center, go to the Concord Chamber of Commerce; open from the end of March until late October, and on the Thanksgiving weekend. Walking tours are available; admission is charged. The Chamber can be reached at 978-369-3120; to access their website, click here. To download a walking map of Concord, click here.
Important non-Revolutionary Concord sites include the Orchard House (home of Louisa May Alcott, where she wrote “Little Women;” admission charge), the Concord Museum (which has one of the two lanterns hung at Old North Church; admission charge), and The Wayside (home to the Alcotts, Nathaniel Hawthorne and Margaret Sidney; admission charge).
Most Revolutionary-centric visitors head directly to the Minuteman National Historical Park to visit the area around North Bridge. It is about 1/2 mile from the town center. For more on the Minuteman Park, see below.
For public transportation from Boston to Lexington, take the MBTA Red line to Alewife station and connect with either the #76 or #62 buses to Lexington. The ride from Alewife to Lexington is about 25 minutes. For the MBTA website, click here.
To Concord center, take the MBTA Commuter Rail from Boston’s North Station. The Fitchburg Line train stops at the Concord Depot on Thoreau Street. From the Depot, the North Bridge is a 1.5-mile walk.
For visitors to both Lexington and Concord traveling without cars, the best option is to travel to Lexington and take the Liberty Ride trolley mentioned above. The trolley stops near all major sites in both towns and provides hop-on and off service, giving the opportunity to hike portions of the Battle Road. It runs on weekends in April and May, then daily until October 28. Adult tickets are $25, children 5-17 are $10. It also includes admission to the Lexington houses mentioned above. For Liberty Ride information, call 781 781-862-0500, website here.
Minuteman National Historical Park
North Bridge seen from the NPS Visitor Center
The Minuteman National Historical Park, run by the National Park Service, has two sections. The eastern section follows the Battle Road from just outside Lexington into Concord. The western section covers the area around North Bridge, just beyond Concord center. Both have visitor centers and ranger-guided tours and talks. All programs are free, with the exception of an admission charge to the Wayside; $5 for adults, free for children 16 and under. For full park information visit the NPS website here or call 978-369-6993. For an interesting website on the Battle Road, click here.
The visitor center at the eastern end of the park (nearest Lexington) features a very good multi-media show, “The Road to Revolution,” especially entertaining for children. The center also has exhibits, dioramas, and other battle-related information. Rangers are on duty to answer questions and there is a small gift shop.
The five mile Battle Road makes for a great hike and much of it has been restored to a state similar to Revolutionary times. Be sure to visit the Hartwell Tavern, which is representative of an authentic period home-tavern and has ranger-programs from May through October. The Paul Revere Capture Site, just off Route 2A, is a frequent visitor stop.
West of Battle Road, and the closest stop to Concord center, is The Wayside. In Revolutionary times, The Wayside was home to the muster master of the Concord Minute Men. Later, it became the “Home of Authors,” with its residents including Louisa May Alcott, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Harriett Lothrop (Margaret Sidney). As of this update, the Wayside has been closed for renovations. The Wayside is next door to Orchard House, which charges a separate admission fee and is not associated with the Park.
The western section around North Bridge has a small visitor center set spectacularly on the hill overlooking the bridge. It features a few small exhibits and a very good three dimensional map that illustrates the topography of the important battle sites. It is located in a mansion that once belonged to the Buttrick family. Major John Buttrick was the Patriot who ordered the colonials to fire on the British at North Bridge.
For public transportation to the eastern visitor center from Boston, take the MBTA Red line to Alewife station and connect with the #76 bus to the Old Mass Ave & Marrett Road stop in Lexington. Ask the driver to point out the stop. There is no service on Sunday. To the western section, follow the directions to Concord center, above. The Liberty Ride stops at both sections as well as at Hartwell Tavern, Meriam’s Corner, North Bridge and other park sites.
Adams National Historical Park
Birthplace of John Adams
An easy, rewarding, and often-overlooked Freedom Trail side-trip is to the Adams National Historical Park in Quincy. The park includes the homes of American presidents John Adams (the famous Patriot and 2nd US President), his son, John Quincy Adams (the 6th president), and their descendants from 1720 to 1927. The park is right off of the MBTA Red line and is a simple, quick, and inexpensive trip from Boston. The park is open from mid-April until mid-November. Check their website here or call 617-770-1175. For a web-translation of this section, click here.
A visit starts at the NPS visitor center – access to the homes is only permitted via ranger-led tours. Tours run two hours and cost $5 for adults; children under 16 and holders of a National Park America the Beautiful Passes are free. Before leaving the visitor center, view the excellent short film, “Enduring Legacy,” that overviews the Adams’ lives and accomplishments – it is excellent.
The first stop is at the presidents’ birthplaces. To start, you will visit the wonderful, sparse, “saltbox” house (c. 1681) where John was born in 1735. Only 75 feet away is the house where John and Abigail gave birth to John Quincy in 1767. That house also holds the law office where John drafted the Massachusetts Constitution, which later served as the model for the US Constitution.
The next stop is at the “Old House.” Built in 1731, it was purchased by John and Abigail as a more suitable residence after their return from John’s diplomatic posting to London in 1788. The Adams family expanded the home from its original seven rooms to what you visit today. It was also home to John Quincy, his son Charles Francis (ambassador to Great Britain during the Civil War) and their descendants. It served as a summer White House and is full of original family artifacts and art that helps tell the Adams’ story – a real treasure to visit.
Next door to the Old House, set in a beautiful garden, is the Stone Library, built in 1873. This serves as the John Quincy Adams presidential library and holds over 14,000 books, artifacts and family paintings.
Across the street from the visitor center, but not part of the National Park, is the United First Parish Church. The Church contains the tombs of John, Abigail, John Quincy and Louisa Catherine Adams, website here. Founded in 1636 as a branch of the Puritan church in Boston, this is the fourth Church building erected on this site. Designed by Alexander Paris (also designer of Quincy Market), it was completed in 1828, with granite and funding from John Adams. If you have time, take the brief tour of the church and the crypt; a small donation is requested. Tours are available on the same schedule as the National Historical Park, from mid-April through mid-November.
Boston Harbor Islands
A fantastic trip and relaxing change from Revolutionary Boston is a visit to the Harbor Islands National Recreation Area. At the Islands you can visit a Civil War era fort, swim, picnic, hike, bird watch, camp, enjoy a concert, or just delight on the wonderful, narrated cruise through the Harbor. For the younger visitors there is even a playground with an amazing view of the Boston skyline. The Islands are a cooperative effort between the National Park Service and various Commonwealth, City and private groups.
The park itself features 12 islands and peninsulas, and even the oldest active lighthouse station in the United States (used since 1716, only accessible via a special “Lighthouse Tour”); practically, you can visit a maximum of two Islands per day – visiting a single Island requires at least ½ day, but don’t rush. There is a snack shack with a seafood menu on Georges Island, but the food quality can be variable – so you may want to pack a lunch. There is an expertly-staffed pavilion on the Rose Kennedy Greenway between Quincy Market and Long Wharf to help plan your visit, purchase ferry tickets, etc.
Although ferries run from several suburban locations, most visitors will take the ferry the north side of Long Wharf (by Christopher Columbus Park); the ferries take you to either George’s or Spectacle Island. From George’s Island, during the summer, there are connections to other islands. Fares are: Adults, $15; children 4-11, $9; over 65, $11, inter-island, $3. Regular service runs May through Columbus Day in the fall, but there are various winter visit opportunities. Definitely visit the website for current and detailed visiting and transportation information.
There is a very well done Visitor Center on Georges Island with interpretive exhibits highlighting the Islands’ history, their role in the defense of Boston, the impacts of changing military technology, even the respective diets of enlisted men and officers – fascinating even for the non-military-oriented visitor. Unless you know you want your stop to be Spectacle Island, stop here first, watch the eight minute video and plan the rest of your visit. Rangers are there to help.
There are excellent Ranger-led tours of the Civil War era Fort Warren, which was built between 1833 and 1861 (self-guided tours are also available). During the Civil War, the fort served as a prison for over 1,000 Confederate personnel, the most famous the Confederate Vice President Alexander Stephens. Fort Warren remained active through the Spanish-American War and World War I. During World War II, it was part of the harbor’s defense from German U-boats. Over the years it was modified to accommodate changing cannon technology. It was permanently decommissioned in the 1950’s when guided missiles obsoleted cannon for coastal defense.
A visit is highly recommended and suitable for all ages. Handicap access, however, is limited; please check the website for detailed information.
Useful links for a Boston Harbor Islands visit:
-
The official Boston Harbor Islands website.
-
National Park Service website.
-
National Park Service map of the Islands, download here.
-
Boston Harbor Islands YouTube channel, here.
-
Ferry website.
-
The Boston Harbor Island Alliance website.























