Select your language to auto-translate:
Map © 2008 DeLorme (www.delorme.com) TOPO USA® – Annotations by the Author
By the time white Europeans arrived, New England had been inhabited by Native Americans for over a thousand years. Migrating here after the retreat of the last ice age, by 1500 they had a population likely in excess of 100,000. Originally hunters and gatherers, they had become more agricultural – with extensive fields of corn (maize), beans, and squash. By this time the tribes were fundamentally stationary, but shifted dwellings several times year based on weather – winter, autumn hunting, and summer.
The New England tribes had a common heritage and belonged to the Algonquian family. Their language was fairly common, and although each tribe had nuances, there was the ability to be understood from Cape Cod to Canada.
Politically, each tribe and sub-tribe had a single primary ruler, called “sachem” or “sagamore”. These sachem were usually men, but sometimes there were squaw, or female, sachem. Within the tribal hierarchy, there were sub-sachems for functions such as the military (for war), powwows (medicine), and other functions.
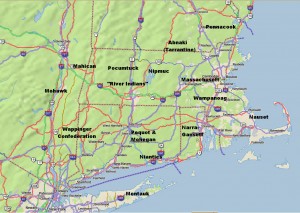
At the time of the white man’s arrival, there were a number of principle tribes, many peaceful, but some warlike and in competition with their neighbors. The names of these tribes have been inherited by many New England towns, rivers and lakes. Those tribes included:
- The Abnaki, also known as the Tarrantine to other tribes, inhabited western Maine, especially the Kennebec Androscoggin & Saco River valleys, as well as portions of neighboring New Hampshire. As this is the colder and more mountainous portion of New England, the Abnaki tended more to hunting than farming. More warlike than their southern neighbors, many tribes, and particularly the Massachusetts, lived in dread of Tarrantine raids. They had a reputation for cruelty and were accused of cannibalism by the English.
- The Penacook inhabited southern and central MA, northeastern MA and southeastern ME, with the principle subdivision around Concord, NH. The Penacook had many subordinate tribes including the Nashua, Piscataqua, and the Winnepesaukee.
- The Massachusett (in Algonquian, “people of the great hills”), from whom the state of Massachusetts got its name, inhabited the eastern area of state, around Boston. Originally one of the more powerful tribes, it was devastated by the plague and wars with the Abnaki. Their population declined from about 3,000 to 500 between 1615 and 1630.
- The Wampanoag inhabited the areas of southeastern Massachusetts near where the Pilgrims landed in current Plymouth. They were also devastated by the plague. Metacom (King Philip of “King Philip’s War”) was Wampanoag.
- The Narragansetts were a powerful tribe that lived in present-day Rhode Island.
- The Niantics were a largely coastal tribe lived on Narragansett Bay, and extended as far west as the Pequot tribe in Connecticut.
- The Pequots, of eastern Connecticut were originally part of the Mahican (known as Mohegan, a corruption of the Mahigan name) a tribe of the of upper Hudson River valley in New York. They were warlike and aggressive and the primary protagonist in the Pequot War in 1637-1638.
- The Nipmucs who inhabited central MA, were a comparatively weak tribe who frequently paid tribute to their neighbors.
- The Pocumtucks were a loose association of tribes that lived west of the Nipmucks in the areas around Deerfield, MA.
- South of the Pocumtucks along the Connecticut River Valley lived the “River Indians”, another loose association of tribes.
- Bordering the River Indians to the west was the Wappinger Confederacy, which extended from the west bank of the Hudson River as far south as Manhattan and north to Poughkeepsie. Tribes of the Wappinger included the Mattabesic, Quinnipiac, Paugusset, and Tunxis.
- North of the Wappinger Confederacy were the Mahicans, (Mohecan), the parent tribe to the Pequots. They inhabited the western Connecticut and the upper Hudson Valley in New York.
- The Nausets were a smaller tribe that lived on Cape Cod.
- The Montauks inhabited eastern Long Island.
- The Mohawks, who spanned most of eastern New York State, were the easternmost tribe of the Iroquois confederacy, e.g., they were not Algonquin. Extremely warlike, they were formidable and feared by the Algonquin tribes.
Between 1616 and 1619 a plague, or the “Great Dying,” wiped out almost ¾ of the New England Native American population, with the devastation worse in the coastal areas where mortality was as high as 95%. A major effect was that when white settlers began arriving, starting in 1620, they encountered very little of the indigenous population. The Native American’s ability to resist the Europeans was very weak.
For Part 2, the Early Exploration of New England, click here.
Sources and for additional reading:
Bragdon, Kathleen Joan, Native People of Southern New England, 1500-1650. University of Oklahoma Press, 1996.
Vaughan, Alden T., New England Frontier Puritans and Indians 1620-1675. Little Brown and Company Boston, 1965.
http://iweb.tntech.edu/kosburn/History-201/Puritans%20&%20Indians.htm
http://www.memorialhall.mass.edu/classroom/curriculum_6th/lesson2/bkgdessay.html
http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/squanto.htm